"Parallels in Nature and Business: Lessons from Physiology for Operational Efficiency"
- bryanqalekahle
- Feb 8, 2025
- 2 min read
Introduction
Understanding the principles that govern biological systems can offer valuable insights for business management. One such principle is the concept of resistance in series and parallel arrangements, as seen in the human circulatory system. By exploring these arrangements, we can draw lessons on how to structure decisions and financial strategies in organizations to maximize efficiency and profitability.
Series vs. Parallel Arrangements in Resistance
Total Resistance in Series: In a series arrangement, resistances add up. The total resistance is the sum of individual resistances (R1+R2+R3+...R_1 + R_2 + R_3 + ...):
R total = R1+R2+R3+...R_{total} = R_1 + R_2 + R_3 + ...
Pros:
Simplicity in design.
Easier to manage a single flow path.
Cons:
High total resistance can lead to inefficiencies.
A single failure can disrupt the entire system.
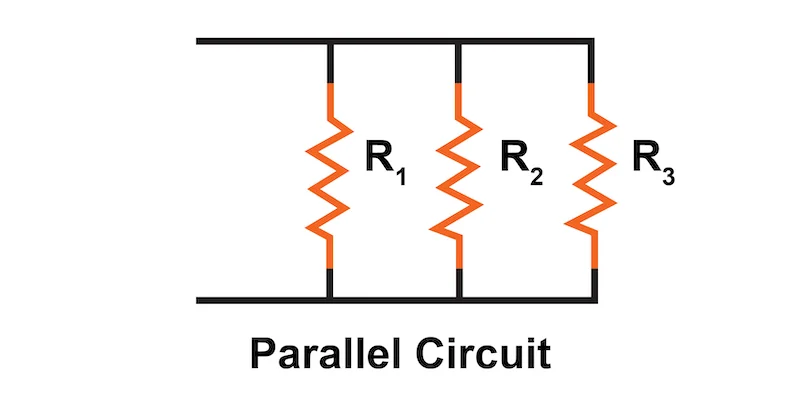
Total Resistance in Parallel: In a parallel arrangement, the total resistance is lower because the inverse of the total resistance is the sum of the inverses of individual resistances (1/R1+1/R2+1/R3+...1/R_1 + 1/R_2 + 1/R_3 + ...):
1Rtotal=1R1+1R2+1R3+...\frac{1}{R_{total}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3} + ...
Pros:
More efficient with lower total resistance.
Flexibility and redundancy; one path's failure doesn't halt the system.
Cons:
Complexity in design and management.
Requires more resources to implement multiple paths.
The Human Circulatory System: A Parallel Design
In the human body, blood vessels are arranged in a parallel structure rather than in series, resulting in decreased Total Peripheral Resistance (TPR) and more efficient blood flow:
Lower TPR: Reduced resistance allows for easier blood flow, ensuring efficient oxygen and nutrient delivery to tissues.
Redundancy: Multiple pathways ensure that if one vessel is blocked or damaged, others can compensate.
Application in Business Decision-Making
Decision-Making and Financial Structuring: Adopting a parallel approach in business can lead to operational efficiency and maximized profits with fewer resources. Here’s how:
Distributed Decision-Making:
Parallel Thinking: Allowing decentralized teams to make decisions independently can reduce bottlenecks and increase agility.
Lower Resistance: Fewer hierarchical barriers result in faster implementation and innovation.
Diversified Investments:
Risk Mitigation: Investing in multiple sectors or projects reduces the risk of total failure, similar to having multiple blood flow paths.
Increased Returns: The overall return is more stable and potentially higher due to diversification.
Resource Allocation:
Efficient Use: Like the parallel arrangement of blood vessels, allocate resources to multiple projects or departments to ensure optimal performance.
Redundancy and Flexibility: Ensure that critical functions have backup resources, preventing disruptions.
Conclusion
By examining the principles of resistance in series and parallel arrangements, as demonstrated by the human circulatory system, businesses can derive valuable lessons for improving efficiency, decision-making, and financial structuring. Emulating the body's parallel design can lead to reduced operational resistance, increased flexibility, and ultimately, greater profitability with optimal resource usage.
Incorporating these physiological insights into business strategies not only enhances organizational resilience but also fosters innovation and growth in a competitive landscape.






Comments